Exploring Space's Most Bizarre and Enigmatic Discoveries
5. Achernar, the Flattest Star
Found Year: 2003
Discoverer: The Very Large Telescope of the European Southern Observatory
Location: Constellation of Eridanus
In 2003, astronomers utilizing the Very Large Telescope (VLT) of the European Southern Observatory made significant strides in our understanding of celestial objects within the Constellation of Eridanus. Through the dramatically enlarged lens of the VLT, stargazers can observe night sky objects with remarkable magnification, revealing details that are invisible to the unaided eye.
While stars may appear circular when viewed without assistance, few are truly perfectly round. The advanced technology of the VLT allows for detailed imaging and analysis, uncovering the complexities and irregularities of stellar shapes. This enhanced perspective challenges our perceptions of what we see in the night sky and offers deeper insights into the nature of stars and their formation.
In conclusion, the observations made with the Very Large Telescope in 2003 not only broadened our understanding of the stars in Eridanus but also exemplify the power of modern telescopic technology in unraveling the mysteries of the universe. As we continue to explore the cosmos, such discoveries remind us of the intricate beauty and diversity of celestial bodies.
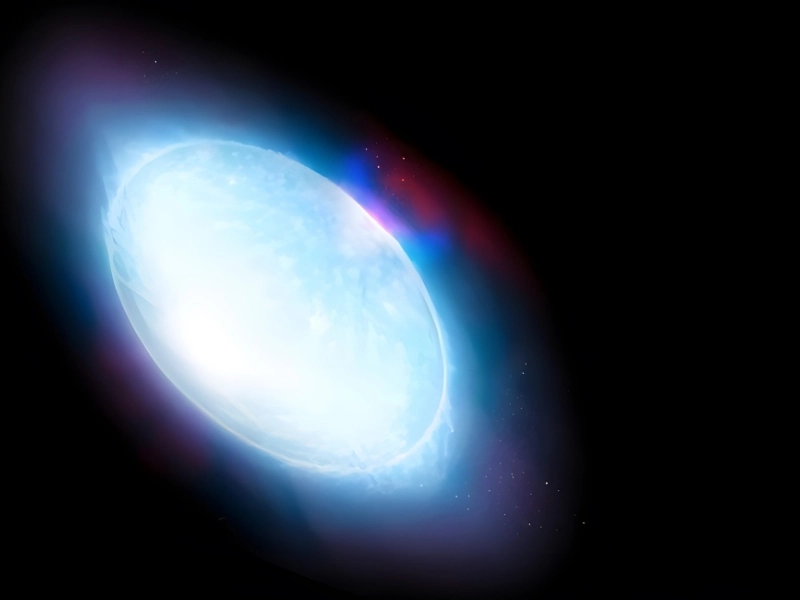

Photo Credit: The Achernar Star Is Flattest ©Pablo Carlos Budassi via Wikipedia
Achernar is not only a non-spherical star in our universe but also holds the distinction of being the flattest star in the Milky Way Galaxy, which has contributed to its fame among astronomers. This unique shape arises from its rapid rotation, which causes the gaseous body to flatten significantly. As a result, Achernar resembles an eclipse more than a traditional spherical star.
The equatorial radius of Achernar is approximately 56% larger than its polar radius, illustrating the dramatic effect of its swift spin on its overall shape. This flattening phenomenon is a fascinating example of how stellar dynamics can influence the physical characteristics of celestial bodies.
In conclusion, Achernar's status as the flattest star in the Milky Way Galaxy not only highlights the diversity of stellar forms but also emphasizes the complexities of star formation and rotation. As we study such unique stars, we gain deeper insights into the processes that govern the behavior and evolution of celestial objects.